Search engine optimization (SEO) used to be defined by the number of keywords and keyword synonyms across your website’s content.
When Google launched its knowledge graph, SEO shifted away from simply relying on keywords, and search engine crawlers began prioritizing rich snippets and entities on search engine results pages (SERPs).
These days, Google has more systems to identify the true meaning of keyword searches and queries. By categorizing ideas into “entities,” Google revolutionized its search proficiency.
While keywords are still important, SEO experts now also use entity-based SEO to further their ranking efforts. Context and relevance are becoming increasingly important in search engine results, and entities can help improve these factors.
In this article, we’ll explain what entities are, how to use them, and what the future of SEO might look like.
What Is Entity-Based SEO?
Entity-based SEO uses context, not just keywords, to help users find the information they seek.
While keywords are an essential part of your SEO strategy, they don’t fully reflect how humans search for information. For example, a person who searches for “Paris” may be looking for Paris Jackson, the city of Paris (in France or Texas), the movie Paris Is Burning, or innumerable other options.
Google offers suggestions for searchers regarding additional context, which serves the dual purpose of speeding up their searches by showing popular options and reminding them to add more context if none of those are what they need.
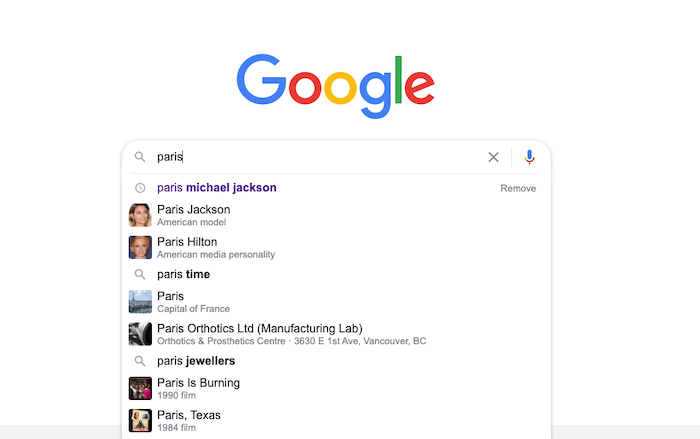
Entity-based SEO is helpful for searchers but slightly has made things a bit more complicated for content creators. Three ways entity-based SEO has changed the landscape include:
- Better mobile capabilities: Entities allowed SEO to improve mobile results. Entities also improved mobile-first indexing, which is more prevalent than desktop searches.
- Translation improvements: Entities can be found regardless of homonyms, synonyms, and foreign language use thanks to context clues. For instance, a search for “red” will include results for “rouge” or “rojo,” if the searcher’s settings allow for this.
- Rich snippets: Rich snippets, which include things like photos and customer ratings as part of their results, generally outperform even number one search results.
Keywords Vs. Entities: What’s the Difference?
Entities might sound similar to keywords. In fact, they are quite different. Here’s how they differ and why those differences are so important.
Keywords
Keywords are words or phrases used in searches. They’re often the focal points of terms users search for and can be questions, sentences, or single words.
For example, users looking for makeup tutorials may search for makeup, tutorial, smokey eye, how to do a smokey eye, and so on.
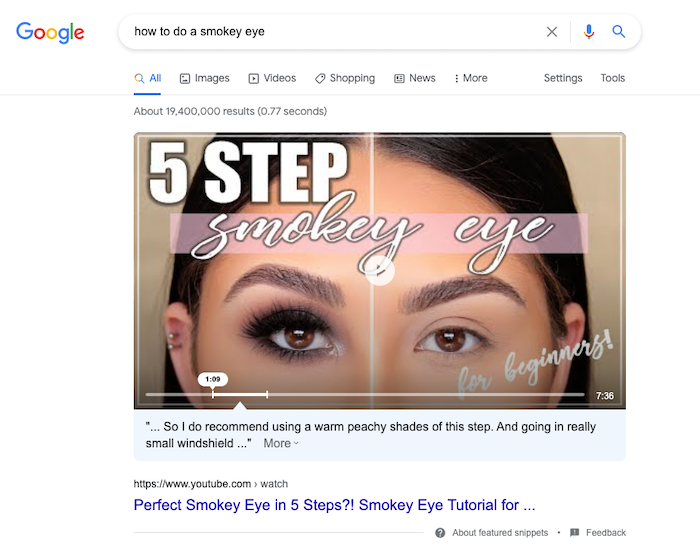
Keywords still matter because they connect your content to queries. Your goal is to drive organic traffic to your site by ranking for keywords that help customers find your brand on search engines.
Keywords have long been the backbone of SEO, mainly because search engine algorithms needed clear, concise direction to populate relevant search results.
In the early days of SEO, keyword stuffing, which involves adding your chosen keyword far too many times or including largely irrelevant, popular keywords, was used constantly. At the time, search algorithms needed to see specific keywords repeatedly to rank content properly.
These days, algorithms have evolved significantly, and many old SEO tactics are, at best, frowned upon.
Google has always maintained that good copy and content are preferred over keyword stuffing and other black-hat SEO tricks.
Entities
As defined by Google, an entity is “A thing or concept that is singular, unique, well-defined and distinguishable.” This doesn’t need to be a physical object and can include colors, dates, ideas, and so on.
Entities can be people, places, products, companies, or abstract concepts. They should always be distinct and independent of other entities or keywords.
Emphasizing entities over keywords has allowed search engines to be more accurate in their results. However, search engines aren’t psychic—they need more information to figure out which entity you’re searching for.
For example, a search for the word “apple” could result in pages about the fruit or pages about the company. As interesting as both topics are, if you’re searching for information about whether apple seeds are indeed poisonous, reading about iPhones probably won’t be too helpful. You need to add some keywords to tell the search engine which entity you mean.

We can think of entities as large topics keywords live within. For entities to be legitimate, they need to link to a search engine knowledge graph representing linked information and data across the internet. Knowledge graphs allow search engines to scan your website effectively.
Google’s Knowledge Graph used Wikipedia as its primary trusted seed set. An easy way to think about entities is that they are anything that could have a specific Wikipedia page assigned to it.
It’s important to note that not every entity has a Wikipedia page. This could just be a helpful way to think of the concept.
How Do Entities and Keywords Work Together?
Keywords with context help entities become defined, but you need to know precisely what your entity is all about before you can create your keyword-rich and well-written content. An SEO strategy recognizing both factors is your best bet for success.
On-page, you can create entities for an internal knowledge graph that uses keywords to link to different pages on your site. You can also connect your content to high E-A-T knowledge graphs such as Wikipedia or LinkedIn. While this won’t directly affect your page rank, it can improve your page authority in search.
Benefits of Entity-Based SEO
Entity-based SEO is more relevant, refined, and granular than keyword SEO alone.
Over time, improvements in automated natural language processing and new search methods like chatbots and digital assistants have made search queries longer and more complicated.
Yet, most search queries still relate to an entity. For example, “Things to do in Brussels” or “What to do in Brussels today” relates to Brussels, Belgium. Even without the quantifier of Belgium, search engines can tailor their results based on previous entity knowledge and context.
For marketers, entity-based SEO offers more concrete discoverability. Ensuring your brand is a concrete entity could help you include a large number of keywords that may not have been previously available. Nike, for example, can be searched through running shoes, tennis shoes, workout clothes, Air Jordans, and more, without users getting lost along the way.
In e-commerce, entity-based SEO can connect your products under a single entity. For example, if you sell windows in Paris, France, you may be able to contribute keywords to the Paris, France entity, opening up your business to potential new clients. Also, connecting your window selling business to Paris, France, helps ensure customers living in Paris, Texas, won’t see your content and mistakenly order from you.
How to Shift Your Strategy to Entity-Based SEO
Adding an entity focus to your existing SEO strategies could help you prepare for future algorithm updates.
Understanding which entities your business connects to and establishing your business as an entity in itself will become increasingly important in coming years.
How do you move on from previous, often keyword-focused strategies to an entity-based strategy?
List Your Business on Relevant Directories
One way to leverage entity-based SEO is to list your business on directories across the internet. Google My Business, for example, is used as a data source for the Google Knowledge Graph.
Other listing services, such as Yelp, can also help create strong, domain-rich backlinks for your brand and help you create a known entity. Yelp appears in the top five search results in 92 percent of Google web searches.
Listing sites may change from location to location, so do your research when deciding where to list. Additionally, be sure to choose sites with high domain authority to improve your search engine standing.
Using this strategy, businesses listed here can form entities and begin connecting unique keywords.
Prioritize Brand Building
Brand building is another essential tactic in entity-based SEO. Any offline brand presence measures need to be brought online, and you should always be considering new ways to create a well-defined and unique identity for your brand.
Managing your reputation is also increasingly important, as your reputation may factor into entity creation. Be conscious of the keywords you currently rank for and note—and correct for—any possible PR problems that could arise.
Consider Your Use of Interface Management Tools
Interface management is becoming a factor in entity-based SEO, as a silo approach to collaboration may negatively impact search engine visibility. This may happen despite keyword rankings, which could significantly affect some businesses.
Ultimately, focusing on keywords is not going to be enough going forward. Businesses and marketers need to shift their focus to entity-based SEO and start implementing tactics to ensure their content connects to their entities.
Conclusion
Entity-based SEO can be a great way to communicate the context and relevance of your brand online.
By targeting ideas and context rather than words or phrases alone, entities build a bigger picture of your content, potentially allowing it to out-perform traditional keyword research methods.
We can expect to see more opportunities for marketers to create more depth in their branding strategies by focusing on entity-based SEO.
In what ways have you experimented with entity-based SEO?
Did you miss our previous article...
https://consumernewsnetwork.com/technology-news/7-tips-for-creating-international-ppc-ads






