If you’re retailing products and want to reach the widest audience possible, having a well-optimized e-commerce website is an absolute must.
Why? Well, there are several benefits.
A great e-commerce website helps you understand the basics about your customers, for example, demographics like their locations, age groups, and how they found you.
By using tracking, you can then use your visitor’s information for behavior analysis to get to know them even better.
An e-commerce website does more than this, though. It can also help you understand where things are going wrong. For example, which traffic sources don’t work, which offers don’t appeal, and cart abandonment issues and their potential causes.
Of course, the more obvious reason you would want to have your site fully optimized: the growth of e-commerce worldwide. Year on year, e-commerce keeps growing, and this pattern looks like it will continue.
If you’re already online, that’s great. However, you risk remaining invisible to fresh prospects and new leads if you don’t take proactive steps to increase visibility.
How do you do that? It’s simple enough: with SEO for e-commerce.
What Is SEO for E-Commerce?
SEO for e-commerce is a strategy that helps web retailers rank higher in search engine results. A well-designed and optimized website with high-quality content will rank better in search engines such as Google, increasing your store’s visibility and driving traffic.
In other words, SEO for e-commerce concentrates on optimizing your site, which makes it easier to get leads and conversions.
However, unlike SEO for content-focused websites, SEO for e-commerce is more than just adding keywords, writing blog posts, and gaining links. You need to understand how search engines work and what they reward.
That means having a working knowledge of SEO for e-commerce, considering Google’s guidelines, analyzing buyer intent, and implementing it strategically.
E-Commerce SEO Best Practices
E-commerce for SEO is a complex field, and with millions of online retail sites in existence, it’s not always easy to make your site stand out.
While it might seem like a huge challenge to build your SEO rankings, you can make a positive start by applying some best practices. In time, this increases your chances of visibility and gaining more organic leads and customers.
For the unfamiliar, what do best practices for SEO for e-commerce look like? Well, you could start by addressing fundamentals like:
- navigation
- internal links
- avoiding clutter
- creating unique content
- including alt text for images
However, there’s far more you can do. Below, explore our list of SEO for e-commerce best practices you can implement today.
1. Perform Keyword Research the Right Way
There are many different ways to optimize your e-commerce site, and not every approach is suitable for every site or product. However, some guidelines apply to every online retailer, and one of them is performing keyword research correctly.
Yes, you want the most relevant and popular keywords in your industry, but you must also understand buyer intent.
Keyword intent is the intention behind a search query. You can identify it by looking at the specific phrases and terms people use when looking for an item online.
There are two main types of keyword intent you see most often.
Informational Keyword Intent
Informational keyword intent is used in SEO to describe the type of information the searcher is looking for.
These types of searches usually consist of:
- How tos: These are searches that contain questions such as “how do I?”
- Direct purchase: These involve searches with keywords like “buy this.”
- Factual queries: These use words such as “fact” and “information” when a searcher wants more details about a subject.
Commercial Keyword Intent
Commercial keyword intent is when people are looking for information to help them make a purchase. This means that they want to find what they need and buy it as fast as possible.
Consumers typically use commercial keyword intents when they know what they want but don’t know where to find it yet. You see this when you’re typing specific terms into Google like “buy digital camera” or “find new laptop deals.”
Commercial keyword users typically have more intent to purchase and are less likely to search for information about the product or service than just researching where to find it.
Determining Keyword Intent
Deciding consumers’ keyword intent seems challenging, but you can make it easier on yourself. For example, AgencyAnalytics breaks it down into stages.
- Analyzing SERPs: Pay special attention to paid ads, knowledge graph results, and organic listings.
- Look at Google ads for commercial intent: Seeing bid prices for keywords gives an idea of how competitive keywords are.
- Review your analytics: Look for content with high bounce rates as it may mean it doesn’t match with searcher intent.
You could also use keyword tools like Google’s keyword planner. Others you can try include:
Ubersuggest
Ubersuggest is a free online tool that can find long-tail and related words to any topic or keyword, or you can opt for the paid version.
This tool is great for content writers, bloggers, copywriters, and marketers who want to generate new content ideas or find out what users are searching for about a given topic.
Features include:
- backlink data
- rank tracking
- site audit reports
Backlink Data
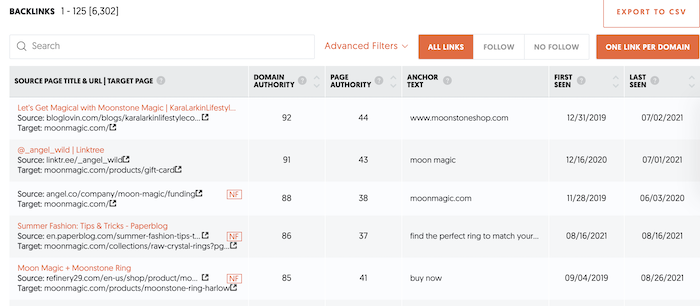
To see what backlinks you are getting from other sites, go to the backlink analyzer under SEO Explorer. This can help you see who is already a fan and what related sites you can target for more linkbuilding.
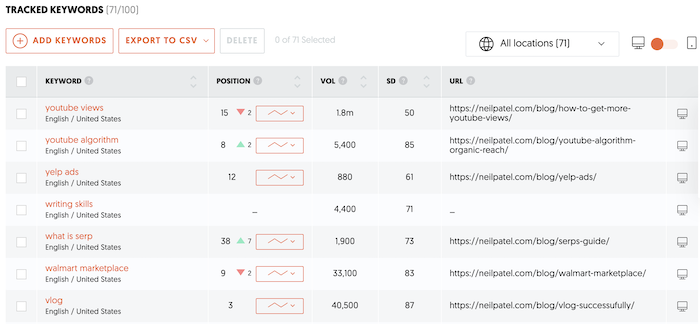
Rank Tracking
See how you rank in organic SERPs for your target keywords with Ubersuggest rank tracking. That way, you can see how you have improved over time. This is under Dashboard on the left side.
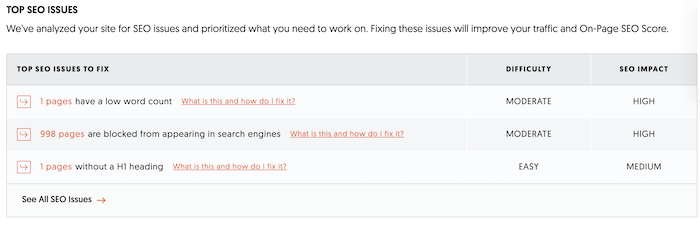
Site Audit
Run a site audit to track what issues need to be fixed on your site that could be affecting user experience and organic traffic. Think of the audit as a starting point, then review it regularly to make sure you’re fixing other issues. This is under the SEO Analyzer section. One the audit has run, it will tell you your top SEO issues and how to fix them.
It also has a free chrome extension to do keyword research while you’re conducting Google or YouTube searches.
Answer the Public
Answer the Public is a great tool. It lets you uncover what people all over the world are curious about and going through.
Answer the Public is intuitive, too. Just enter your keyword on the homepage to understand precisely what people are asking. It can also help you find which topics are most popular at any given time, which might be helpful as another tool for keyword research. However, if you want further guidance, there’s a set of tutorials available.
It’s free to use, but you can upgrade to pro for more features. The following example uses “multivitamins.”
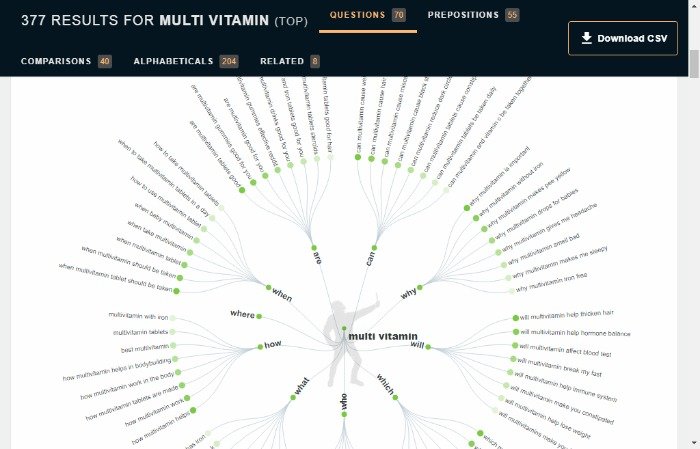
The results give a detailed picture of the kind of questions people are asking and give a better idea of intent.
2. Optimize Product Pages to Improve Ranking
If you want to attract and acquire new customers, look at your on-page user optimization. It matters because it gets your site a higher rank, meaning fresh streams of organic traffic and more conversions.
Not every area of your e-commerce site needs optimizing, so in this section, let’s focus on the ones that matter most to online retailers: product descriptions, images, and reviews.
Optimize Your Product Descriptions
A product page is interesting because it has a lot of different features that all need attention. You also want a few things to stand out from the page to gain visitors’ engagement and get them to click through.
To begin optimizing your e-commerce product pages, you need to keep in mind three key aspects:
- What are the most crucial things on the page?
- How can you maximize visibility and impact with these elements?
- How can you use this information to improve your product description’s effectiveness?
Now, start looking at what you can do to maximize the impact of your product descriptions. This could be things like.
- adding multiple, high-quality, unique images
- including keywords
- including detailed, keyword-rich descriptions
- adding calls to action (CTAs)
- including testimonials
Optimize Your Images
A sometimes neglected area of SEO for e-commerce is images. Photos are an excellent way to communicate a message and draw in an audience. However, they can also distract people from the message you are trying to convey, so be careful not to use too many images and crowd your descriptions.
Although quality images are vital to show your goods at their best, there’s more to it than that. Optimizing your images for SEO will give you higher search engine rankings and more traffic from potential customers and may gain you traffic from social media channels.
Here are some pointers for optimizing your images:
- Choose suitable images for your platform. Your host usually specifies optimal image sizes and other image guidelines.
- Provide captions with alt tags for pictures.
- Use the right keywords in file names.
Feature Reviews
Reviews provide a snippet of information that helps shoppers weigh whether to go with a particular product or store.
Reviews are vital for success in e-commerce as so many people rely on them. Additionally, they help you build trust with your potential customers and improve conversion rates.
You can encourage customers to leave reviews by sending automated messages whenever they purchase. You can also set up email campaigns to send out reminders or offers once they have left a review on your site.
Before moving on, here are more optimization tips:
- Use canonical tags to link duplicate product pages and similar group products together.
- Create a well-written page that includes the necessary information about the product, an image of the product, and a video of it in action.
- Include at least one CTA on your product page. For example, “Add To Cart” or “Check Availability.”
- Make sure you include shipping details and policies upfront so customers know what they’re paying from the start.
3. Make Sure Your Site Is User Friendly
UX stands for user experience. You can enhance UX by good design, making the aesthetics more visually appealing.
However, it’s not just about making a website look good; it’s about making it work well. UX includes everything from navigation, ease of use, and the overall “feel” of the website.
UX is also about making sure people can find what they are looking for, keeping them engaged while browsing, and giving visitors the best experience possible.
You may not think that UX affects SEO, but the interaction between the two began some years ago, and UX is also imperative for discoverability.
Additionally, recent changes mean that UX is soon to be a Google ranking factor. According to Search Engine Land, that means if Google thinks your website offers visitors a bad experience, it may rank lower. Google measures the new ranking with “Core Web Vitals” and has set out its guidelines online.
Many things can influence UX, but a few key factors are apparent:
- Ads shouldn’t interfere with the user’s view of content.
- Your site should load quickly and be mobile-friendly.
- Any website should be clutter-free and easy to navigate.
- You should include CTAs, so customers know what to do next.
Finally, use consistent styling throughout, and make it accessible.
4. Don’t Forget Long-Tail Keywords
You usually see long-tail keywords on the right side of a search engine results page (SERP).
A long-tail keyword is a term that typically has low search volume but still meets the criteria for relevancy to your business. They also tend to convert well because they’re a better match for what the searcher is looking for, and they typically give higher traffic.
For those reasons, you shouldn’t be afraid to rank for long-tail keywords because they’re a valuable source of traffic.
Long-tail keywords are great for:
- competitive niches
- increased conversion rates
- ranking new sites more easily
You can find long-tail keywords by using Google’s “People also ask” or use a free keyword tool like Ubersuggest. There are plenty of other tools available too.
The following example uses Wordtracker, where the search for “dumbells” delivered this:
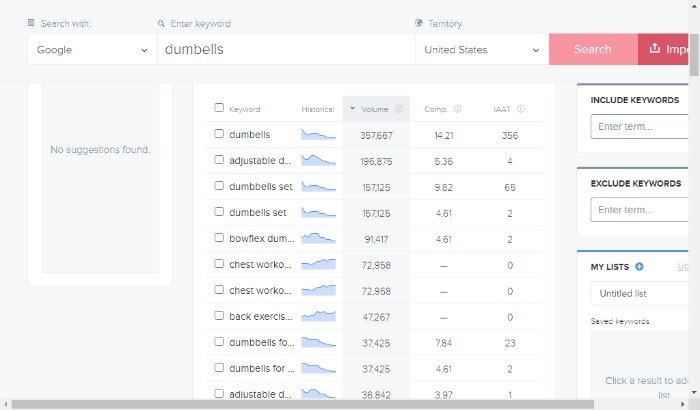
As you can see, they give you a firm idea of what your customer is looking for and of their intentions.
5. Use a Simple URL Structure
There are more detailed guides on URL structures, but this section gives you the basics.
A simple URL structure not only enhances the user experience but also improves your SEO e-commerce efforts to some extent.
Additionally, when your e-commerce site has a simple URL structure, it’s easier to share products on social media and other websites, and it can improve SEO for e-commerce as it provides more relevant data for search engines.
For the best results, URLs should be as readable and understandable as possible.
For instance, here’s an example of what NOT to do: https://www.example.com/article-about-hiking/
It would be much better to use this URL structure: https://www.example.com/hiking-articles
Google also has some advice on improving URL structure.
Additionally, you can:
Use Keywords
Search engines scan the URL and use the keywords in the URL to determine where that page should rank in the SERPs. The keywords in the URL are called “metatags” and help tell search engines what the content or topic of that page is.
That’s why you must spend some time thinking about your keywords before deciding on a URL structure.
When people search for your business online, they often type in the precise words they’re looking for. As an example, a person may type in “online shoe store” into a search engine.
Therefore, when someone types in “online shoe store,” it’s crucial those words are somewhere in your URL structure.
Use Breadcrumbs
Breadcrumbs are a navigational tool. They allow website visitors to retrace previous steps and return to where they started. Breadcrumbs are not just a usability technique but also provide additional SEO benefits.
For example, if you visit a blog post from your main homepage, the breadcrumb for that post would be “Home > Blog > This Post.”
You find breadcrumbs in many web design tools, and you can add them by using markup tags or via JavaScript.
Avoid Stop Words
Common stop words are “the,” “and,” “of,” and “a.”
Stop words can decrease your content’s readability and may lower your SEO rankings.
In addition, stop words are less likely to hold a reader’s interest. By removing these words from your website, you can use those spaces for more creative and relevant copy.
6. Use Schema Markups to Help Google and Users Understand Content
Schema markups are HTML tags that provide additional information about the content on web pages. By using these markups, it can improve your SEO for e-commerce efforts.
When you use schema markup, it produces rich snippets. These are a way for search engines to show more information about specific items in the search results.
They also help people find what they are looking for faster and easier by showing different types of information.
There are many different types of rich snippets, such as:
- product markup snippets
- music snippets
- review snippets
The kinds of e-commerce schema are:
- Product schema: This is an extension for products, services, and organizations. It enables discovering new products and services in web search queries by providing rich product information such as images, price, and availability. Product schema also allows the display of product ads on the SERPs.
- Review schema: This enables online reviews. The author and title filters allow you to find specific people who have written reviews on your website or blog post and for searchers to find product reviews.
- Product availability schema: The product availability schema is a list of products that are available to purchase. It can be a single page, or it can be within an online store. Such lists typically detail the product name, description, price, images, and variants.
- Video schema: Video schema is a type of metadata used to describe the content and format. For example, video schema may include the audio language, video resolution, or age rating of the video.
- Price schema: Price schema is a technique for the pricing of products or a price range.
7. Avoid Duplicate Pages and Content
Have you ever visited a website and got the feeling you’ve read it all somewhere before? That’s all too common with production descriptions and category descriptions when online retailers use duplicate product catalogs and images.
It’s understandable why e-commerce sellers just republish the same descriptions. Usually, it’s simply because they don’t have the resources to produce fresh content themselves.
However, even if you don’t have time to rewrite everything, you can still significantly reduce the amount of duplication on your site in product descriptions and other areas.
For instance, by
- using a CMS with site-wide 301 redirects or adding canonical tags on every page that you know might have duplicates (pages with similar titles, pages that share an identical URL, etc.)
- adding a suffix to the URL
- using different product images
- adding unique keywords on other pages
8. Don’t Let Page Speed Kill Your Ranking
Website page speed loading time is the measurement of how long it takes for an internet user to open a web page. You can measure it by adding up the time to download all the non-hidden assets, such as images, scripts, and stylesheets.
Page speed is a ranking factor, and survey after survey shows consumers aren’t willing to wait around while a site loads.
Web-users say their ideal site speed is just two seconds, but the faster, the better. If you’re not sure about your current speeds, you can test it at Cloudflare or try Google’s tool.
What should you do if your site is too slow? First, you need to find the reason. It could be:
- Your site simply has too much content for your server to handle.
- Too many scripts are slowing down load times.
- Images take an excessive amount of time to load.
- There’s a problem with your web host.
While not all e-commerce site owners can guarantee a perfect 100 percent on Google’s PageSpeed Insights, you can try and fasten load times by:
- having fewer images on the pages
- compressing files
- using fewer social media widgets
- optimizing your images
- avoiding clutter and using plenty of white space
- limiting redirects and HTTP requests
- fastening your server response time
Additionally, you might want to think about changing web hosts or upgrading your hosting package to accommodate your needs better.
9. Content Does Matter for E-Commerce
E-commerce isn’t just about images and keywords. Written content should also be part of your SEO for e-commerce strategy.
Posting regular content not only attracts organic traffic. It can gain your customers’ trust, boost your website rankings, and solidify your reputation as an expert in your niche too.
There are many types of content you can focus on:
- sharing how-to pieces and answering FAQs
- new product launches and anything newsworthy
- a glossary page
- including user-generated content (UGC)
- testimonials and launches
- video demonstrations and Q and As
- webinars
For more ideas, take it a step further and get to know your audience so you understand their main concerns and problems. This allows you to write content that addresses their everyday worries and offer products that solve these.
Now you’ve got some ideas for content. However, content isn’t worthwhile without a strategy behind it. Let’s break it down:
- Get to know your customers better with buyer personas.
- Understand their preferred content. If you’re tracking your content data, you should see which content types get the most views. Additionally, you can ask customers and prospects through surveys or groups.
- Establish a content calendar and create the content.
- Publish the appropriate content for the various stages of the buying cycle.
- Use A/B testing in key areas like titles.
- Measure the results and tweak.
10. Link Building for E-Commerce
Link building is a ranking factor for SEO. Quality links tell Google that your site has credibility. Backlinks also influence how your website ranks for keywords.
Sounds great, doesn’t it? But just how do you go about creating these all-important backlinks?
A few ways to do this are:
- creating internal backlinks
- writing guest posts
- using social media ads
- sharing content on social media
- issuing press releases
- writing blog comments and sharing on forums (if allowed)
- creating infographics and sharing them online
- issuing whitepapers and case studies
These are all legitimate ways to build quality links. Although they can take time, you shouldn’t take shortcuts by buying links. Some paid links violate Google’s guidelines, and if you’re buying cheap links, the quality is usually questionable. Poor quality links lead to lower SERP rankings and reduced traffic, as well as a potential negative impact on your site’s reputation.
11. Add a Sitemap
A sitemap is a visual representation of your website or digital product. It provides visitors with a bird’s eye view of the website and explores different pages.
Your sitemap should detail all of the pages on your site, from category pages to product pages. It should also include all the subcategories, products, and other content within those sections.
You can develop a sitemap manually or use an automated tool such as Google’s Webmaster Tools to generate one. Sitemaps use both XML and HTML, although HTML sitemaps are more helpful to visitors.
Other tools for creating a sitemap are:
Lucid Sitemap Generator
The Lucid chart sitemap generator is a user-friendly tool that makes creating a sitemap for your website easy. It has many features, like adding categories and subcategories.
Powermapper
Powermapper is an easy-to-use tool for creating and updating sitemaps and allows you to generate one-click checkouts.
It’s a web-based tool with no coding expertise required. However, there is a fee.
12. Make Social Sharing Easy
Google’s Matt Cutts once said that social sharing doesn’t impact SEO, but many would disagree.
While social media sharing may not directly affect your SEO, sharing your content on social media increases brand exposure and gets people more familiar with your business.
Further, the more mentions you get on social media, the more influence this can have on your SEO by:
- driving organic traffic and increasing visibility
- improving local SEO
- expanding your content reach and enhancing brand recognition
- increasing backlinks
If you want an easy way to increase your shares on social media, consider getting a tool like Buffer or Hootsuite to automatically post content from your site across all of your social media accounts at scheduled intervals.
Frequently Asked Questions About SEO for E-Commerce
How do I Find the Right Keywords For my E-commerce Store?
There are several free resources that you can use to find keyword ideas, such as Google AdWords, Ubersuggest, and Google’s Keyword Tool. You should also look at what your competitors are using to find the best keywords for their audience.
Finally, avoid using broad keywords that generate many clicks but don’t provide much conversion value. Use long-tail keywords where you can.
How Much Does SEO for E-Commerce Cost?
The cost of SEO depends on many factors, including the number of keywords targeted, competitive landscape, and how much effort you need to optimize each page for ranking.
It’s not easy to put a price tag on SEO because it depends on how many resources you allocate and what you want to achieve. To help you budget, Search Engine Journal provides an SEO budget calculator.
What Is SEO for E-Commerce?
SEO for e-commerce is the process of optimizing a website so that it can rank more highly in search engines. Several factors affect how well a website ranks on the SERPs, such as the quality and relevance of the content, the use of appropriate keywords to optimize the site, and the site’s load speed.
How Is SEO for E-Commerce Different?
When it comes to SEO for e-commerce, there are different areas you need to focus on, such as optimizing:
- product pages and descriptions
- diversifying product content and information
- images on your website
- your homepage
SEO for E-Commerce Conclusion
SEO for e-commerce helps boost your website visibility, brings new queries and customers, and helps build your loyal audience.
It may seem like there’s a lot to think about. However, by concentrating on the main SEO best practices and optimizing the critical areas of your website, it doesn’t have to be as complicated as it sounds.
The most important thing to remember is SEO for e-commerce doesn’t happen overnight. Instead, it’s an ongoing strategy that requires updating as you go to get the optimum results.
What is your experience of SEO for e-commerce? Tell us below.






